Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
What is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
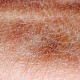
Discoid lupus erythematosus is a chronic skin condition which consists of sores that are inflamed with scarring. They have a crusty and scaly appearance, and often times the center is a lighter colour with a dark rim on the outside. The rash will usually be raised and does not itch. They usually appear on the face, ears, and scalp, but have been seen on the body as well. Most commonly it is seen on the nose and cheeks. If the lesions develop on an area of the skin with hair, such as beards, scarring and hair loss could take place. Changes in skin pigmentation will take place with this autoimmune disorder. Woman are more likely than men to have Discoid Lupus Erythematosus (DLE) by 3 to 1 . It is seen most commonly in the age group of 20 to 40 years of age. Between 17 to 48 out of every 100,000 people will have DLE. Often times discoid lupus erythematosus will run in families.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Symptoms
Symptoms of discoid lupus erythematosus include inflammation of the skin and a rash. Other symptoms that could be seen on either a daily occasion or from time to time include hair loss, permanent scarring or red patches that are disc shaped on the skin that are crusty and scaly. Other symptoms that could be life threatening include chest pain or pressure, pale or blue lips, irregular heartbeat, inability to urinate, rapid heart rate, or difficulty breathing or rapid breathing. If one has been diagnosed with DLE, and any of these symptoms are occurring, seek medical attention asap.
The Cause of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
There is no known cause of Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. However, this autoimmune disorder is believed that possible risk factors include exposure to sunlight and cigarette smoke. Complications from DLE include scarring that could be permanent as well as secondary infections of the skin or surrounding tissues.
Treatments available for Discoid Lupus Erythematosus
A biopsy will usually be done on the skin to determine if the skin lesion is Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. Further blood work may be needed .
Treatments for Discoid Lupus Erythematosus could include corticosteroid drugs that can be used either topically or injected into the skin lesion. Injections of cortisone are usually more effective than a cortisone ointment, but the ointment will slow down the progression of the skin lesion and improve them in appearance. Very potent forms of corticosteroid drugs will be needed for the lesions. One study has found that fluocinonide cream is very effective at treating those with DLE, and could possibly be more effective than hydro cortisone. It has been found that systematic steroids do not seem to be that effective. If systematic steroids are needed, hydroxycholoquine is one that is often used. Patients who use hydroxycholoquine need an eye exam once a year to prevent damage to the retinas of the eye and will also need periodic blood work done. Imiquimod has been proven to be effective in some patients with DLE.
Discoid Lupus Erythematosus Prevention
One with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus can prevent flare ups by applying sunscreen when outdoors. Always apply 30 minutes before sun exposure, and reapply every two hours. Wear sunglasses, hats and protective clothing when exposed to the sun. If you smoke, quit smoking. Reduce your exposure to second hand smoke as well. Keep on track with all follow up appointments with doctors as it is crucial to stop the spread of the disease. These should be taking place every 6 months to a year. At these appointments, the doctor will check to make sure that the disease is not spreading to the internal organs.
With early recognition and treatment, it is possible to live a quality life with Discoid Lupus Erythematosus. With early treatment, it will be possible to eliminate the scarring in many cases.
Reference Sources:



Leave a Comment/Share your Story
Want to join the discussion?