Cellulitis
What is Cellulitis?
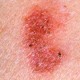
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection. It appears as a red, swollen area of the skin. It is hot to the touch and feels tender. It has a tendency to spread fast over the body. The lower legs are most commonly effected by cellulitis in adults, although it can occur anywhere on the body, even the face. In children, it commonly affects the face and the anus. It effects the surface of the skin, and in some cases effects the tissues underlying the skin, spreading to the bloodstream and the lymph nodes. If not treated, it can spread and be fatal.
Cellulitis Symptoms
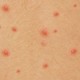
Symptoms of cellulitis include redness, swelling, tenderness, fever, warmth, and pain. The redness of an area may spread over time. Red spots that are small can appear on top of the reddened skin, and small blisters might appear and then burst. If you have a fever, you will want to get medical attention asap, or if you have a rash that is tender, red and swollen or changing rapidly. Muscle aches and pain, as well as chills could signal an infection of the skin. Fatigue and general ill feeling may accompany these. Nausea and vomiting, hair loss at the site of the infection, and joint stiffness caused by swelling of the tissue over the joint are all symptoms of cellulitis as well.
How does Cellulitis spread?
Cellulitis appears on the skin when bacteria enters the skin through a crack. It commonly happens on the legs, with bacteria entering where there was a recent surgery, where there is an ulcer, a cut, a wound, athletes foot or dermatitis. People that have recently got a tattoo or piercing should be concerned about cellulitis. Those who have weakened immune systems are susceptible to cellulitis as well. Do note that certain spider bites and insect bites can transmit the bacteria that starts cellulitis. Dry, flaky skin or swollen skin can also be an entry point for the bacteria to enter.
Other Skin Conditions and Diseases Associated to Cellulitis
There are many risk factors associated with cellulitis. Those include skin conditions such as shingles, chicken pox, athletes foot, and eczema. When breaks appear in the skin, there is a place for the bacteria to enter. Swelling of the arms or legs may result in swollen skin the cracks. If one has had cellulitis before, they are more prone to get it again. If one is obese, this increases the likely that they will not only get cellulitis, but have repeat episodes.
Cellulitis Treatment and Prevention
An exam of the skin will be needed to determine if you have cellulitis. Often times no other testing is done, however in some cases a blood culture, a complete blood count, or a culture of any other fluid inside the effected area may be done. It will be treated with antibiotics. Usually within 3 days, the cellulitis should start looking better. If it does not, let the doctor know. Usually a round of antibiotics will be prescribed for up to 14 days. Keep taking the prescribed meds even if you do feel better or the skin clears up. If the infection becomes severe, one may need to be hospitalized to have IV antibiotics to go directly into the bloodstream. The effected area will need to be rested, and dead skin tissue may need to be cut away.
One can prevent cellulitis from happening. Keep the skin clean and take good care of it. Prevent skin from cracking by applying lotion. If you have diabetes, check the feet and legs often. If you do have a wound, wash it daily with warm water and soap. Dry well and then apply an antibiotic cream. Be on the lookout for signs of infection, such as drainage, redness and pain.
Reference Sources:
1. Royal Childrens Hospital Melbourne
2. National Institutes of Health



Leave a Comment/Share your Story
Want to join the discussion?